Monetary Policy Report - October 2025
The Monetary Policy Report presents the Bank's technical staff's analysis of the economy and the inflationary situation and its medium and long-term outlook. Based on it, it makes a recommendation to the Board of Directors on the monetary policy stance. This report is published on the second business day following the Board of Directors' meetings in January, April, July, and October.
In the third quarter, inflation rose and was higher than expected. The economy continues to grow, mainly driven by household consumption and the recovery of certain segments of investment. Employment has also remained strong, and the unemployment rate is at historically low levels. Although international uncertainty has reduced, some risks associated with geopolitical conflicts and trade tensions remain.
In this context, the Board of Directors maintains a cautious monetary policy, allowing inflation to continue moving toward the 3 % target and supporting the gradual recovery of economic growth.
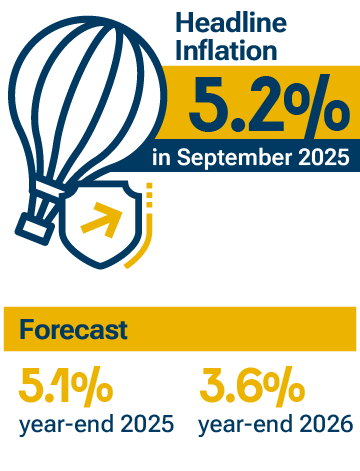
Prices increased more than expected during the third quarter of the year. However, inflation is still expected to decrease in 2026 and fall within the range of 2 % to 4 %, continuing to approach the 3 % target, but at a somewhat slower pace. It is estimated that inflation will be at 5.1 % by the end of 2025 and at 3.6 % in December 2026.
- After some months of relative stability, headline inflation rose during the third quarter and reached 5.2 % in September. Core inflation, excluding prices that fluctuate most frequently (food and regulated items), remained stable at around 4.8 %.
- This increase in overall inflation is explained by greater adjustments in food prices, especially perishables food, and in the prices of goods. These changes occurred amid strong consumption, labor cost pressures, and some supply restrictions.
- Inflation in September was higher than expected due to surprises in the prices of food, goods, and services. The largest upward surprises were in food, and to a lesser extent, in some goods and services. This happened despite a lower-than-expected dollar price.
- It is expected that monetary policy actions and the reduction of some supply-side pressures on prices will allow inflation to continue declining toward the target over the next two years, although more slowly than estimated in the previous report.
- There remains high uncertainty about future price increases, especially due to the magnitude of the minimum wage increase for 2026, future evolution of the exchange rate, adjustments in energy and gas prices, and possible impacts from geopolitical conflicts and trade tensions, among other factors.
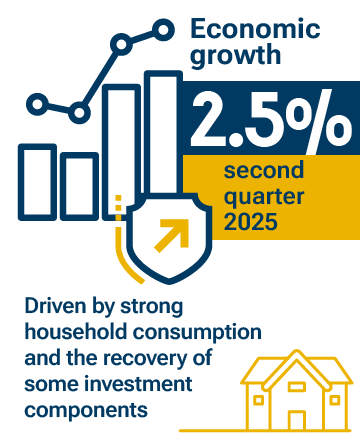
The economy continues to grow, driven by strong household consumption and the recovery of some investment components, in an environment of real increases in disposable income and strong employment performance.
- During the second quarter of 2025, the economy grew by 2.5 %, mainly driven by strong private consumption and the recovery of certain investment segments.
- Household consumption continues to increase, in a context of high employment levels, greater disposable income, significant remittances sent by Colombians living abroad, sustained good income from coffee sector, and increased consumer confidence.
- Investment also increased significantly, especially in machinery and equipment and, to a lesser extent, in infrastructure projects.
- Employment continues to grow significantly, especially in cities. The unemployment rate remained at historically low levels.
- The Colombian economy is expected to continue gaining dynamism, supported by the factors that have recently boosted household disposable income, along with interest rates that would gradually decrease as inflation moves closer to its target.
- However, risks to Colombia’s economic growth remain, associated with uncertainty related to the complex internal fiscal situation and international political and trade tensions.
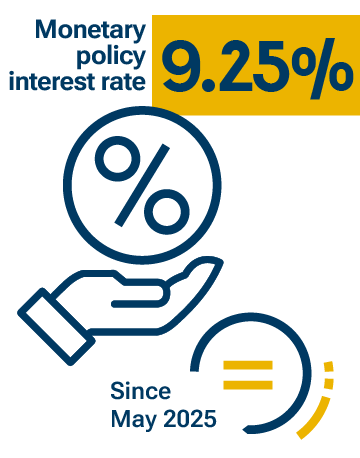
The Board of Directors maintains a cautious approach to monetary policy, compatible with inflation continuing to move toward its 3 % target and with sustainable economic growth.
- Inflation has increased in recent months; it is projected to decrease more slowly than anticipated three months ago and faces significant upward risks going forward.
- Inflation expectations of economic agents have also increased and exceeded 3 % over horizons shorter than five years.
- Economic growth is expected to continue consolidating, and excess productive capacity over demand is expected to decrease by mid-2026.
- In this context, the Board of Directors maintained the monetary policy interest rate at 9.25 % in September and October. A cautious monetary policy is considered appropriate to support the continued decline of inflation toward the 3 % target.
Monetary Policy Presentation (only in Spanish)
Box Index
Box 1: The Macroeconomic Imbalance Index (MII) for Colombia
Perdomo-Sánchez, Darío y Herrera-Pinto, Nicolle Valentina

































































